You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Barrel break in
- Thread starter mark-hunter
- Start date
- Joined
- Apr 13, 2013
- Messages
- 9,474
- Reaction score
- 33,459
- Location
- Delaware, USA
- Media
- 97
- Articles
- 5
- Member of
- Atglen Sportsmen's Club, NRA, SCI
- Hunted
- RSA, DE, NJ, PA, KS, TX, ME
Bartlein barrels does not recommend lapping or fire lapping their barrels.
Break-in and cleaning regimen: https://bartleinbarrels.com/cleaning-and-breaking-in-guide-lines/
Break-in and cleaning regimen: https://bartleinbarrels.com/cleaning-and-breaking-in-guide-lines/
Attachments
Yeah. I like this regimen also....Bartlein barrels does not recommend lapping or fire lapping their barrels.
Break-in and cleaning regimen: https://bartleinbarrels.com/cleaning-and-breaking-in-guide-lines/

JamesJ
AH elite
- Joined
- May 30, 2013
- Messages
- 1,344
- Reaction score
- 879
- Location
- Texas, where else.
- Deals & offers
- 140
- Media
- 140
“Barrel break in” is a scam invented by barrel makers. Talk to a custom gun builder. They don’t break in a barrel before they shoot for groups. They clean them and shoot them. Heck most of the time they don’t even clean them after they’ve been test fired.
Nobody I’m aware of recommends fire lapping, it’s a fast way to ruin a barrel.
Nobody I’m aware of recommends fire lapping, it’s a fast way to ruin a barrel.
“Barrel break in” is a scam invented by barrel makers. Talk to a custom gun builder. They don’t break in a barrel before they shoot for groups. They clean them and shoot them. Heck most of the time they don’t even clean them after they’ve been test fired.
Nobody I’m aware of recommends fire lapping, it’s a fast way to ruin a barrel.
Well that's the problem with these "myths"...they seem to differ from experience to experience...I have a custom gun builder and he not only builds rifles, he still shoots competitions...he breaks in the barrels (as per Kreiger/Bartlein), does not clean much, shoots well, etc. Yet, while he breaks them in, he would not fire lap, he might hand lap a rough one. But a custom barrel he breaks in.
Newboomer
AH legend
I clean a new barrel just to get whatever is in it from the factory out. Then it goes to the range and shoots. I let the barrel cool after a 2 or 3 round group. As far as cleaning on the range, I don't and have never had an accuracy problem even after years of shooting. I do clean after a range session by using solvent, a brush and patches. I store my rifles dry because I don't want oil running down into the action and I don't always remember to run a patch before going out.
Kind of what Jerry Miculek says. "Break in? Just shoot it --hard."
Kind of what Jerry Miculek says. "Break in? Just shoot it --hard."
Newboomer
AH legend
Good plain old Windex works wonders on black powder fouling.With black powder cleaning right after shooting is a must. The good part? Hot water is perfect for removing corrosive salts.
Bob Nelson 35Whelen
AH ambassador
- Joined
- Oct 28, 2018
- Messages
- 11,487
- Reaction score
- 28,474
- Location
- Wyong new south Wales Australia
- Media
- 130
- Member of
- SSAA
- Hunted
- Australia
375 Ruger FanKrieger video
Krieger barrel break in https://kriegerbarrels.com/faq#breakin
- What is the best way to break-in and clean a Krieger Barrel?
Background:
Below are our recommendations for proper break in and cleaning of a barrel. The information below is meant as a guideline and not meant as step by step instructions. If you have a better way that works for you without damaging the bore or using improper chemicals, by all means continue to use your methods. Many successful competitive shooters will use these instructions to the letter, some will disagree.
LONG & SHORT TERM STORAGE:
Your Krieger barrel has been shipped to you with a SHORT TERM rust inhibitor sprayed in the bore to protect it from corrosion during shipping. Upon receipt of your barrel, you should first review the order confirmation and/or packing list to make sure the barrel matches the specifications you ordered. The very next thing you should do is clean the bore and apply a bore protectant suitable for the length of time it will be stored. This can range from a light gun oil all the way up to a preservative grease or cosmoline. The same should be done after a barrel is fit to your rifle.
Preventing oxidation/corrosion in the barrel is the responsibility of the customer. We cannot be responsible for a barrel that has been improperly stored, neglected, or abused by either the end customer, gunsmith, or a distributor.
BREAK-IN & CLEANING:
With any premium barrel that has been finish lapped -- such as your Krieger Barrel --, the lay or direction of the finish is in the direction of the bullet travel, so fouling is minimal compared to a barrel with internal tooling marks. This is true of any properly finish-lapped barrel regardless of how it is rifled. If it is not finish-lapped, there will be reamer marks left in the bore that are directly across the direction of the bullet travel. This occurs even in a button-rifled barrel as the button cannot completely iron out these reamer marks.
Because the lay of the finish is in the direction of the bullet travel, very little is done to the bore during break-in, but the throat is another story. When your barrel is chambered, by necessity there are reamer marks left in the throat that are across the lands, i.e. across the direction of the bullet travel. In a new barrel they are very distinct; much like the teeth on a very fine file.
When the bullet is forced into the throat, copper dust is removed from the jacket material and released into the gas which at this temperature and pressure is actually a plasma. The copper dust is vaporized in this plasma and is carried down the barrel. As the gas expands and cools, the copper comes out of suspension and is deposited in the bore. This makes it appear as if the source of the fouling is the bore when it is actually for the most part the new throat.
If this copper is allowed to stay in the bore, and subsequent bullets and deposits are fired over it, copper which adheres well to itself, will build up quickly and may be difficult to remove later. So when we break in a barrel, our goal is to get the throat “polished without allowing copper to build up in the bore. This is the reasoning for the fire-one-shot-and-clean procedure.
Every barrel will vary slightly in how many rounds they take to break in For example a chrome moly barrel may take longer to break in than stainless steel because it is more abrasion resistant even though it is a similar hardness. Also chrome moly has a little more of an affinity for copper than stainless steel so it will usually show a little more color if you are using a chemical cleaner. Rim Fire barrels can take an extremely long time to break in, sometimes requiring several hundred rounds or more. But cleaning can be lengthened to every 25-50 rounds. The break-in procedure and the cleaning procedure are really the same except for the frequency. Remember the goal is to get or keep the barrel clean while breaking in the throat with bullets being fired over it.
Finally, the best way to tell if the barrel is broken in is to observe the patches; i.e. when the fouling is reduced. This is better than some set number of cycles of shoot and clean as many owners report practically no fouling after the first few shots, and more break-in would be pointless. Conversely, if more is required, a set number would not address that either. Besides, cleaning is not a completely benign procedure so it should be done carefully and no more than necessary.
CLEANING:
This section on cleaning is not intended to be a detailed instruction, but rather to point out a few do's and don'ts. Instructions furnished with bore cleaners, equipment, etc. should be followed unless they would conflict with these do's and don'ts.
You should use a good quality one piece coated cleaning rod with a freely rotating handle and a rod guide that fits both your receiver raceway and the rod snugly. How straight and how snug? The object is to make sure the rod cannot touch the bore. With M14/M1 Garand barrels a good rod and muzzle guide set-up is especially important as all the cleaning must be done from the muzzle. Even slight damage to the barrel crown is extremely detrimental to accuracy.
There are two basic types of bore cleaners, chemical and abrasive. The chemical cleaners are usually a blend of various ingredients including oils, solvents, and ammonia (in copper solvents). The abrasive cleaners generally contain no chemical solvents and are an oil, wax, or grease base with an extremely fine abrasive such as chalk, clay, or gypsum.
We recommend the use of good quality, name brand chemical cleaners on a proper fitting patch/jag combination for your particular bore size and good quality properly sized nylon or bronze brushes.
So what is the proper way to use them? First, not all chemical cleaners are compatible with each other. Some, when used together can cause severe pitting of the barrel, even stainless steel barrels. It is fine to use two different cleaners as long as you completely dry the bore of the first cleaner from the barrel before cleaning with the second. And, of course, never mix them in the same bottle. NOTE: Some copper solvents contain a high percentage of ammonia. This makes them a great copper solvent, but if left in the bore too long, can damage/corrode the steel. Do not leave these chemicals in a bore any longer than 10-15 minutes MAXIMUM! DO NOT EVER use straight ammonia to clean a barrel.
Follow instructions on the bottle as far as soak time, etc. Always clean from the breech whenever possible, pushing the patch up to the muzzle and then back without completely exiting the muzzle. If you exit the muzzle, the rod is going to touch the bore and be dragged back in across the crown followed by the patch or brush. Try to avoid dragging items in and out of the muzzle, it will eventually cause uneven wear of the crown. Accuracy will suffer and this can lead you to believe the barrel is shot out, when in fact, it still may have a lot of serviceable life left. A barrel with a worn or damaged crown can be re-crowned and accuracy will usually return. Have the crown checked by a competent gunsmith before giving up on a barrel that may otherwise be in good condition.
This information is intended to touch on the critical areas of break-in and cleaning and is not intended as a complete, step-by-step guide or recommendation of any product. Use a quality one piece cleaning rod that is either vinyl coated or carbon fiber, a rod guide proper for the action you are cleaning, and chemicals, jags, patches, and brushes that you have determined work best for you. There is no right answer to cleaning products and equipment, however under no circumstances should you use a stainless brush. If you choose to use brushes in your cleaning use only quality bronze phosphor brushes or nylon. Clean them after every use to extend their life. Copper solvents will dissolve a bronze brush rather quickly.
BREAK IN:
The following is a guide to break-in based on our experience. This is not a hard and fast rule, only a guide. Some barrel, chamber, bullet, primer, powder, pressure, velocity etc. combinations may require more cycles some less. It is a good idea to just observe what the barrel is telling you with its fouling pattern and the patches. But once it is broken in, there is no need to continue breaking it in.
Initially you should perform the shoot-one-shot-and-clean cycle for five shots. If fouling hasn't reduced, fire five more cycles and so on until fouling begins to drop off. At that point shoot three shots before cleaning and observe. If fouling is reduced, fire five shots before cleaning. Do not be alarmed if your seating depth gets longer during break in. This is typical of the “high spots in the throat being knocked down during this procedure. It is not uncommon for throat length to grow .005-.030 from a fresh unfired chamber during break in.
Stainless
- 5-10 one-shot cycles
- 1 three-shot cycle
- 1 five-shot cycle
Chrome moly
- 5 - 25 - one-shot cycles
- 2 - three-shot cycles
- 1 - five-shot cycle
I found this years ago on the Legacy Sports (Howa importer) website.
HOWA RIFLE RECOMMENDED BREAK-IN PROCEDURE
Please do not sight-in and or group the rifle during the break-in procedure.
For the first ten shots we recommend using copper jacketed factory ammo. Clean the oil and powder residue out of the barrel before each shot using a commercial bore cleaner with an ammonia content. After firing each cartridge, use a good bore cleaner (one with ammonia) to remove fouling from the barrel using only a soaked patch. We do not recommend anything with an abrasive in it since you are trying to seal the barrel, not keep it agitated.
For the first ten rounds, clean and let the barrel cool between each round fired using a patch and rod only.
Following the initial ten shots, you then may shoot 2 rounds, cleaning between each pair of shots. This is simply insuring that the burnishing process has been completed. In theory, you are closing the pores of the barrel metal that have been opened and exposed due to the manufacturing process.
To keep the temperature cool in the barrel, wait at least 5 minutes between break-in shots. The barrel must remain cool during the break-in procedure. If the barrel is allowed to heat up during the break-in, it will impede the steel’s ability to develop a home registration point, or memory. It will have a tendency to make the barrel “walk” or “climb” when it heats up in the future. If you take a little time in the beginning and do it right, you will be much more pleased with the performance of your barrel in the future.
I got tired just reading this.
My son's Howa 308 was cleaned out before we shot it to remove factory preservatives. We shot it at the range to sight it in,,took it home and cleaned it after about 50 shots. Hunted for a few trips just oiled the barrel between hunts.
Before we went to Namibia the bore was cleaned and a load with 150grain accubonds was chosen. The first group was just over 0.3 inch the next was still less than 0.5 inch. Rifle was oiled and taken to Namibia and shot everything he wanted. The rifle still hasn't been cleaned after 150 shots and still groups 0.5 inch.
All my rifles have had the same treatment just shoot and when accuracy falls off to what is usual I clean it.
I have never and will never run a barrel in.
- Joined
- Jun 14, 2015
- Messages
- 7,640
- Reaction score
- 20,268
- Location
- Shreveport, Louisiana
- Media
- 274
- Articles
- 5
- Member of
- NRA, DSC
- Hunted
- Nam, Zam, Zim,RSA (Eastern Cape & NW), Canada, NZ, Alaska, TX, LA, MO, OH, MT, ID, WA, WY
@Bob Nelson 35Whelen , sounds like you get great results with what you are doing, so why change.
One question though: Do you shoot a rifle that has an oiled barrel? I usually don't. I will store a gun with a lightly oiled barrel, but before going to the range or hunting I will run a patch with Windex and then a dry patch.
One question though: Do you shoot a rifle that has an oiled barrel? I usually don't. I will store a gun with a lightly oiled barrel, but before going to the range or hunting I will run a patch with Windex and then a dry patch.
CoElkHunter
AH ambassador
Interesting thread? I guess I'm just a gun cleaning heathen? I shoot a box of bullets (well ten rounds with the Lott), let some Gunslick Foaming Bore cleaner sit in the barrel for twenty minutes, patch it out, bronze bore brush the barrel ten times. Whatever copper is left in the barrel, I figure it belongs there and has filled in the microscopic imperfections in the steel barrel. Since copper is slicker than steel, maybe the bullets will travel faster down the barrel? Besides, the copper (especially the monometal Barnes) looks pretty against the blue steel bore? Those Barnes really know how to copper up a barrel! Ha! Ha! Ha!
Bob Nelson 35Whelen
AH ambassador
- Joined
- Oct 28, 2018
- Messages
- 11,487
- Reaction score
- 28,474
- Location
- Wyong new south Wales Australia
- Media
- 130
- Member of
- SSAA
- Hunted
- Australia
375Ruger Fan@Bob Nelson 35Whelen , sounds like you get great results with what you are doing, so why change.
One question though: Do you shoot a rifle that has an oiled barrel? I usually don't. I will store a gun with a lightly oiled barrel, but before going to the range or hunting I will run a patch with Windex and then a dry patch.
Sorry mate forgot to say I always run 2 or 3 patches thru the bore before use. I NEVER shoot a barrel without running a patch.
I also sight in my rifles different to every one else.
I get my rifle sighted the take it home. After that each range session I take 3 rounds. I fire 1 shot from a cold barrel (clean or fouled) Ang check the target if it need adjustment it gets it. After the barrel is completely cool I fire one more and repeat. I then repeat the shot and go home.
The rifle should them be sighted for a cold barrel.
Next range session I fire 1 shot only and it is usually on the money.
My reason for this is I don't know anyone who shoots from a warm barrel so I want my first shot from my COLD barrel to be spot on.
I've seen to many people have a flyer on the first shot because they had a warm barrel when they finished sighting in.
Its the first shot at the animal that counts and I want to know that my first shot is going to be where it is meant to be.
Bob
Bob Nelson 35Whelen
AH ambassador
- Joined
- Oct 28, 2018
- Messages
- 11,487
- Reaction score
- 28,474
- Location
- Wyong new south Wales Australia
- Media
- 130
- Member of
- SSAA
- Hunted
- Australia
HogpatrolOh yeah? Well, there's a special place in hell for you guys that don't break in your barrels. The rooms are lined with copper and old powder residue, a forever reminder of your transgressions.I'm not taking any chances. To me, barrel break in is a religion.
As long as there's a slight smell of Hoppes No9 as well I wouldn't mind that room.
Bob
bruce moulds
AH legend
- Joined
- Aug 10, 2018
- Messages
- 2,871
- Reaction score
- 4,842
the old sharps rifle co recommended to wipe the entire gun with oil, possibly whale oil in those days,, and then rub it all off.
this still leaves a minute film of protection, inside and outside the barrel.
a rifle so protected can be shot straight away, and will not have oil funning down into the action and bedding.
bruce.
this still leaves a minute film of protection, inside and outside the barrel.
a rifle so protected can be shot straight away, and will not have oil funning down into the action and bedding.
bruce.
RayAtkinson
AH fanatic
Ive done it both ways, what I saw was some barrels just shoot better than others, some barrels shoot good with proper break in but some barrels shoot best without ever being cleaned, so what to do. I just figured all barrels get broke in by 100 or so shots anyway, so I dont' break in barrels and I won't keep a gun that won't shoot and inch for 3 at a 100....contrary to the cumudgeon gunsmiths of yesterday who claim todays guns wont shoot and inch, they are full of beans, many of todays rifles will shoot and inch, most of the custom barrels will shoot and inch at 100. Yesterdays guns and barrels would seldom do that, but most can be made to do it with some glass bedding and reload work..Just my two bits.
- Joined
- Apr 13, 2013
- Messages
- 9,474
- Reaction score
- 33,459
- Location
- Delaware, USA
- Media
- 97
- Articles
- 5
- Member of
- Atglen Sportsmen's Club, NRA, SCI
- Hunted
- RSA, DE, NJ, PA, KS, TX, ME
First five shots out of a new Lilja barrel chambered in .223/match reamer. Cleaned it, loaded some rounds that shot good in another rifle and took it to the range. No break-in, these are the first five shots at 100 yds. No cleaning in between shots, the first one flew, the rest stayed fairly close together. Ran some patches and there was very little blue and it cleaned up quickly. Premium barrels are generally like this but some barrels take a handful of patches before the blue quits. I just got lucky with the load.
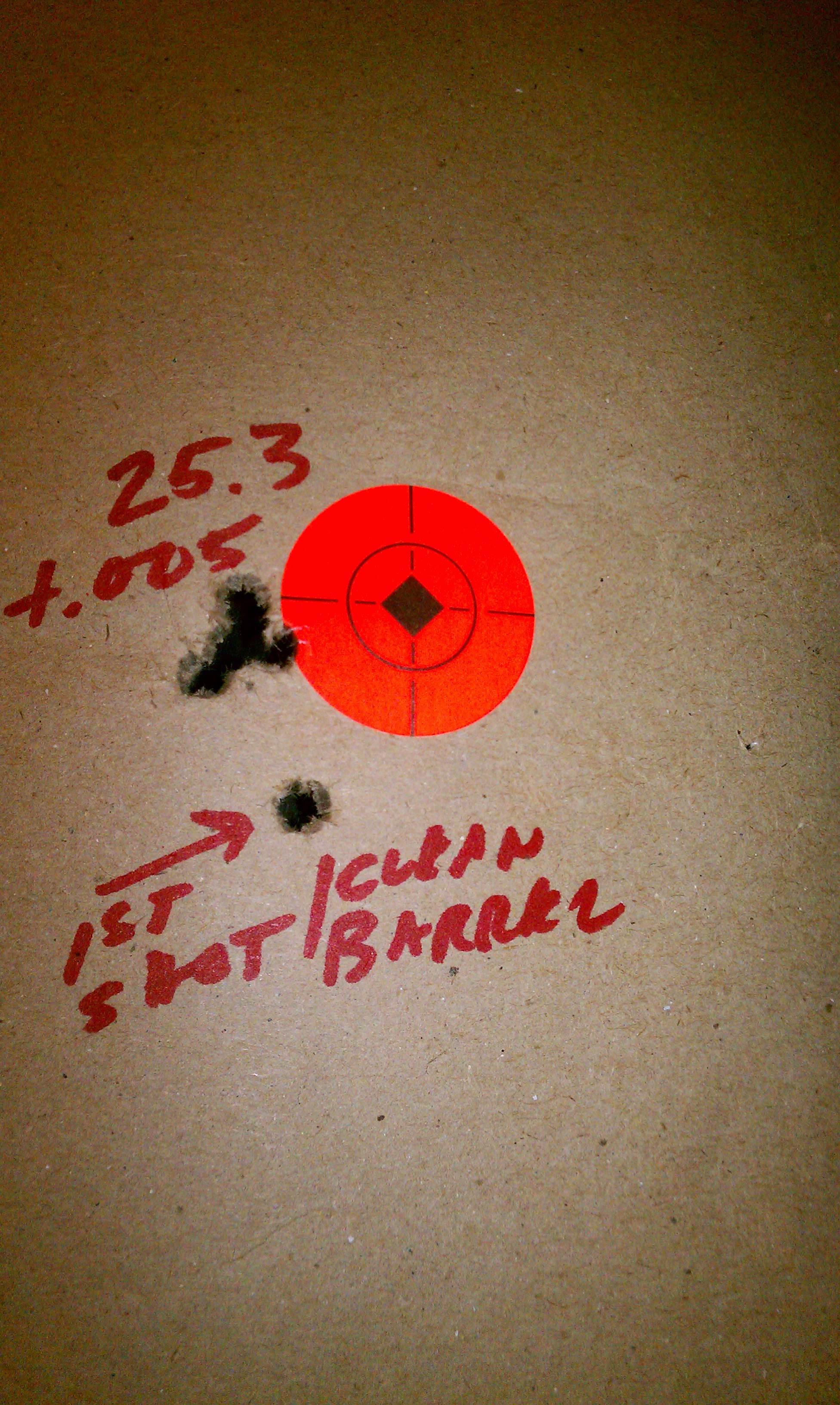

Last edited by a moderator:
Bob Nelson 35Whelen
AH ambassador
- Joined
- Oct 28, 2018
- Messages
- 11,487
- Reaction score
- 28,474
- Location
- Wyong new south Wales Australia
- Media
- 130
- Member of
- SSAA
- Hunted
- Australia
@HogpatrolFirst five shots out of a new Lilja barrel chambered in .223/match reamer. Cleaned it, loaded some rounds that shot good in another rifle and took it to the range. No break-in, these are the first five shots at 100 yds. No cleaning in between shots, the first one flew, the rest stayed fairly close together. Ran some patches and there was very little blue and it cleaned up quickly. Premium barrels are generally like this but some barrels take a handful of patches before the blue quits. I just got lucky with the load.
View attachment 351006
Now you see why I sight my rifles with a cold barrel only. It avoid the first shot flyer
Three shots from my 25. Cold barrel sight in method. 200 yard target 0.86 inch and no fliers
Bob
Goose Cracker
AH enthusiast
I'm one of those suckers that generally follows the break-in procedures. It's my OCD. I can't help it. I'm not sure if it works or not. I do believe it makes subsequent cleanings a bit easier.
I also can't put away a rifle with a dirty barrel. Again the OCD. After a range session or after the end of the season, I thoroughly clean the barrel, run a patch of oil down the barrel, then a clean patch then put it away. I also wipe all the metal down with a very light coat of oil and then wipe it down with a clean rag - similar to what @bruce moulds mentioned.
I will say that @Vanguard2279 introduced me to Wipe-out and I'm not sure I'll ever be the same. That stuff is magic on copper and powder fouling. Cut my cleaning time significantly and leaves the bore shiny as new. But I still run an oiled patch afterwards and then a dry one before the rifle gets put away.
I also can't put away a rifle with a dirty barrel. Again the OCD. After a range session or after the end of the season, I thoroughly clean the barrel, run a patch of oil down the barrel, then a clean patch then put it away. I also wipe all the metal down with a very light coat of oil and then wipe it down with a clean rag - similar to what @bruce moulds mentioned.
I will say that @Vanguard2279 introduced me to Wipe-out and I'm not sure I'll ever be the same. That stuff is magic on copper and powder fouling. Cut my cleaning time significantly and leaves the bore shiny as new. But I still run an oiled patch afterwards and then a dry one before the rifle gets put away.
Rick Cox
AH elite
- Joined
- Dec 17, 2015
- Messages
- 1,394
- Reaction score
- 2,195
- Location
- Armstrong British Colombia
- Media
- 104
- Articles
- 1
- Member of
- Armstrong Fish and Game Club
- Hunted
- Namibia, South Africa, British Colombia Ca.
What is "washing the car"?I also wash my car and change the oil and filter on a regular basis
Bob Nelson 35Whelen
AH ambassador
- Joined
- Oct 28, 2018
- Messages
- 11,487
- Reaction score
- 28,474
- Location
- Wyong new south Wales Australia
- Media
- 130
- Member of
- SSAA
- Hunted
- Australia
@Goose CrackerI'm one of those suckers that generally follows the break-in procedures. It's my OCD. I can't help it. I'm not sure if it works or not. I do believe it makes subsequent cleanings a bit easier.
I also can't put away a rifle with a dirty barrel. Again the OCD. After a range session or after the end of the season, I thoroughly clean the barrel, run a patch of oil down the barrel, then a clean patch then put it away. I also wipe all the metal down with a very light coat of oil and then wipe it down with a clean rag - similar to what @bruce moulds mentioned.
I will say that @Vanguard2279 introduced me to Wipe-out and I'm not sure I'll ever be the same. That stuff is magic on copper and powder fouling. Cut my cleaning time significantly and leaves the bore shiny as new. But I still run an oiled patch afterwards and then a dry one before the rifle gets put away.
Mate when I get home from the range I run a patch soaked in INOX thru the bore and give the whole outside a quick polish with Gilleys gun polish wax and put it in the safe.
After that I go and have the coffee my darling wife has made me while I did it.
Yes it only takes that long.
If I need to clean the bore I use foaming bore cleaner. Great stuff.
Bob
Last edited by a moderator:
Members online
- Nkawu
- CoElkHunter
- outdoorbum
- James Patsis
- Borderer
- HankBuck
- ay2626
- KJE81
- scotinayah
- MBaneACP
- VINOYASADO
- ZG47
- RobBrown505
- Warren Knudsen
- TSALA HUNTING SAFARIS
- krish
- Flewis
- DavidC
- dietcontrungktx
- wildfowler.250
- cperso
- K E Johnson
- ingwe500nitroexpress
- Arthur Morta
- Rimbaud
- Feedratow
- AndreZA
- CZDiesel
- FlowHamed18
- SWARA
- Mopani
- FARO EAST NORTH CAMEROON
- eatmore-pbj
- spike.t
- PerH
- BrowningSafari
- Sunfox
- Carl Pennella
- Sarg
- jpr9954
- Jon Glajchen
- Indigo Earl
- AbdullahB
- Vashper
- a_alrumaidhi
- Jäger_Ivo
- Hunter-Habib
- RSL
- mark-hunter
- NJS416
Total: 68,235 (members: 1,160, guests: 67,075)
Forum statistics
Latest profile posts
Preparing for the adventure of a lifetime. Looking forward to my 2026 Africa hunt with Van Wijk Safaris in South Africa.
What a great way to kick off our 2025 hunting season in South Africa.
This beautiful Impala ram was taken at just over 300 yards, took a few steps and toppled over.
We are looking forward to the next week and a half of hunting with our first client of the year.
This beautiful Impala ram was taken at just over 300 yards, took a few steps and toppled over.
We are looking forward to the next week and a half of hunting with our first client of the year.
Do you have any more copies of African Dangerous Game Cartridges, Author: Pierre van der Walt ? I'm looking for one. Thanks for any information, John [redacted]